Discover the Facts...
What you may not know about oral bacteria and how it relates to overall health
Diabetes results when the body can not produce insulin (type 1) or the body's tissues become resistant to insulin (type 2). The inflammation of the beta cells within the pancreas, which produce insulin, are the basis for both types of diabetes. Recent studies have proven that elevated amounts of oral bacteria, usually also causing gum disease, can raise blood sugar and cause inflammation of the beta cells.
Kumar M, Mishra L, Mohanty R, Nayak R. "Diabetes and gum disease: the diabolic duo". Diabetes Metab Syndr 2014;8:255-8
Gum disease is a condition where the tissues that surround the teeth become inflamed due to infection by certain types of bacteria in the mouth. Dentists call gum disease periodontitis, and is measured by the depth to which they can advance a probe into the space between the gums and the tooth. This technique is called the pocket depth. The deeper the pocket, the worse the gum disease. Testing for the specific types of bacteria that cause gum infections and the resulting inflammation helps dentists better know how to precisely treat gum disease.
Periodontal (gum) disease: causes, symptoms and treatments. NIH publication 13-1142, 2013.
Tooth loss is a consequence of advanced gum disease. The problem begins with infection that resides in the space between the teeth and gums (periodontium). As the infection worsens, the body responds with needed but sometimes destructive inflammation due to selected type of bacteria. Over time, the ligament that attaches a tooth to the underlying jaw bones, is loosened and may even dissolve, which results in the loosening of that tooth. Managing the gum infection, first by testing for the specific bacteria involved, and then having your dentist tailoring the specific treatment, will prevent tooth loss.
Baumer, A, Pretzl, B, Cosgarea, R, Kim, TS, Reitmeir, P, Eickholz, P, Dannewitz, B. Tooth loss in aggressive periodontitis after active periodontal therapy: patient-related and tooth-related prognostic factors J Clin Periodontol. 2011 Jul;38(7):644-51.
One cause of bad breath or halitosis are bacteria that produce sulphur containing chemicals, a by-product of the chemicals metabolism process. Many of the bacteria causing gum disease have this capability. Lowering the levels of bacteria such as Treponema denticola, Td, and Porphyromonas gingivalis, Pg and Prevotella intermedia, Pi will lessen the causes of bad breath.
Kapoor, U; Sharma, G; Juneja, M; Nagpal, A (2016). "Halitosis: Current concepts on etiology, diagnosis and management.". European journal of dentistry. 10 (2): 292-300
Dental decay is also called dental caries, or cavities for short. The decay starts at the tooth enamel. An opening in the enamel either a pit or crevice, can be further dissolved by the acid produced by certain bacteria in the mouth, most importantly- Streptococcus mutans. Higher levels of this bacteria creates more risk of new or worsening cavities. Lowering the amount of Streptococcus mutans in the mouth, mostly through good tooth brushing and reduced consumption of sugary foods, will help prevent cavities.
Hardie JM (May 1982). "The microbiology of dental caries". Dent Update. 9 (4): 199-200, 202-4, 206-8.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition of the immune system. The inflammation which spurs this form of joint disease is caused by autoimmunity, or the body reacting against itself. Heightened levels of total body inflammation worsen rheumatoid arthritis, and the cause of that inflammation is in part due to oral bacteria. In a recent study, persons with mouth infections involving Porphyromonas gingivalis, Pg, and Fusobacterium nucleatum, Fn, have a significantly increased risk of developing rheumatoid disease.
Johansson L, Sherina N, Kharlamova N, et al. Concentration of antibodies against Porphyromonas gingivalis is increased before the onset of symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 2016;18:201
Infections of the gums is caused by a variety of bacteria. The inflammation that results from gum infection can also lead to the spread of those bacteria elsewhere in the body. A cause of atherosclerosis, involving large blood vessels in the heart and in the neck, are one of the places these oral bacteria can land. These bacteria cause local inflammation and the risk of forming unwanted blood clots. A stroke is caused when blood clots, arising from these areas of diseased blood vessels, break loose and migrate to the brain, where they cut of the blood supply to that area of the brain. In this way, oral bacteria are involved in strokes.
Dorfer, CE, Becher, H, Ziegler, CM, Kaiser, C, Lutz, R, Jorss, D, Lichy, C, Buggle, F, Bultmann, S, Preusch, M, Grau, AJ. The association of gingivitis and periodontitis with ischemic stroke J Clin Periodontol. 2004 May;31(5):396-401.
A heart attack is triggered by the blockage of one of the arteries that supply the heart muscle with oxygen rich blood. Occlusion of the coronary arteries are now known to be caused not only by deposition of bad cholesterol, but by the migration and entrapment of oral bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis, or Pg. In a recent review article by Drs. Brad Bale and Amy Doneen, they describe how oral bacteria can no longer be viewed as associated with heart attacks, but as a cause.
Bale, BF, Doneen, A L, Vigerust, DJ. High-risk periodontal pathogens contribute to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis Postgrad Med J. 2017 Apr;93(1098):215-220.
Fusobacterium nucleatum, or Fn, is associated with risk to infect the mother's blood and the placenta. Presence of Fn can cause premature delivery of the baby, lower birth weight and at the same time problems for the mother such as high blood pressure and kidney failure.
Han YK. Fusobacterium: A commensal turned pathogen. Curr Opinion Microbiol 2015, 23: 141-147.
Why Test with OralDNA®?
- Find hidden oral pathogens that threaten your oral and systemic health. Common pathogens directly cause gum disease and may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, stroke and birth complications
- Learn if you were born with gene markers associated with increased inflammation, a critical factor in the severity of periodontitis, diabetes and cardiovascular disease
- Help your provider select the most effective treatment if you already have periodontal disease, and then measure treatment results with a follow-up test
- Learn if you have HPV high-risk types associated with oral cancer
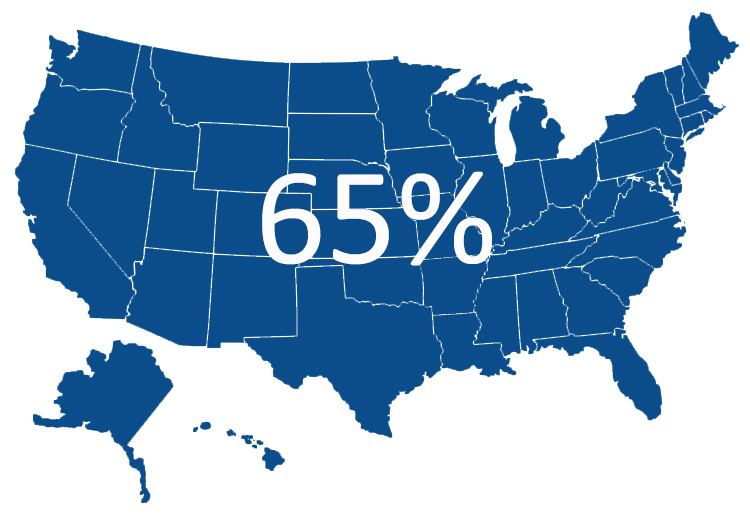
Did you know?
The Oral Cancer Foundation states that HPV is the leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers. In fact 65% of oral cancers are linked to HPV.
OralDNA® Infectious Testing Options: